3. Installation and first-time use¶
This chapter described the installation steps that are required to use the ComFLOW package. The program has been designed to reduce the number of installation steps and on Windows can even be run directly by means of the ComFLOW Command Prompt.
3.1. Licensing¶
A license file is required to unlock the ComFLOW executables. ComFLOW automatically looks for a license in the following order:
- at the location provided in the environment variable
$COMFLOW_LICENSE - in the binary folder of the ComFLOW distribution, using e.g. search pattern
$COMFLOW_DIR/bin/linux/license_*on Linux
Note
Under no circumstances rename the license file or modify its contents, because this will invalidate the license.
3.2. Installation on Linux¶
To prepare everything for a first simulation, the following steps have to be taken.
Unzip the ComFLOW deliverables in some installation directory, e.g.
~/comflow.(This step may be skipped if the deliverables were unpacked from a TAR GZ file.) Make sure the ComFLOW executables have executable rights. Go to the subdirectory
bin/linuxand apply the commandchmod +x *to change the flags for all executable files.In order for the system to find the ComFLOW executables the ComFLOW installation needs to be added to the system search path
$PATH. There exists various ways to do so, using either the bash setup script or environment module provided in the ComFLOW distribution:Persistent installation (recommended)
Include the following lines in your log-on script (typically stored in
~/.bashrc)export COMFLOW_DIR=~/comflow # <-- main ComFLOW folder source $COMFLOW_DIR/bin/linux/comflowsetup.sh # <-- installation script
The environment variable
COMFLOW_DIRshould be set to the main folder of the ComFLOW installation (without the trailing/). The installation scriptcomflowsetup.shtakes care of all the initialization steps.Non-persistent installation (not recommended)
It is also possible to invoke the installation script manually after system startup in a similar manner as described above. However, the installation will only persist in the console in which the installation script was run. The step needs to be repeated upon system restart or change of console.
Environment modules (recommended alternative)
A sample environment module is provided in the root folder of the ComFLOW distribution, which may be used to automatically apply the required setup. The following snippet illustrates the steps required for loading the ComFLOW environment module:
sudo apt-get install tcl # prerequisite: one time only sudo apt-get install environment-modules # prerequisite: one time only module load $COMFLOW_DIR/comflow.tcl
Note
Depending on the configuration of your system the environment module or bash setup script may have to be adjusted.
Install the license file by placing it next to the ComFLOW executables or by setting the environment variable
$COMFLOW_LICENSE.Install dependencies
- Python 3.x
- Paraview (5.6 or newer is recommended)
3.3. Installation on Windows¶
The Windows version of ComFLOW can be used without installation by means of the ComFLOW command prompt.
To get started, unzip the ComFLOW deliverables in the desired installation directory, e.g. in C:\Program Files\ComFLOW.
The ComFLOW command prompt comflowprompt.bat is located in the subdirectory
bin/win64. It is recommended to create a shortcut and for example place it
in the Start Menu or Desktop folder.
A Visual Basic script is provided to generate a shortcut to the ComFLOW command prompt (double click the file bin\win64\createshortcuts.vbs in the Windows Explorer).
By default the ComFLOW command prompt opens in the subdirectory with example simulations examples (or similar).
This behavior can be changed by modifying the ‘Working directory’ property of the shortcut.
During the first run of the ComFLOW command prompt, a default ComFLOW distribution is selected which is available via the commands comflow and geodef.
In order to change the selected version type the command setcomflowversion and follow the instructions on the screen.
Note
- If you want the ComFLOW executables to be available system-wide without intervention of the ComFLOW command prompt, ask your system administrator to place the desired ComFLOW executables on the system search path.
- In order to use the XMF module via the ComFLOW command prompt, no extra steps have to be taken. For system-wide installation it is necessary to set several environment variables in a similar fashion as in the code of
comflowprompt.bat. Ask your system administrator.
3.4. Installing the Paraview post-processing plugins¶
The ComFLOW plugins for Paraview rely on the ComFLOW Python library, which can be
found in the subfolder $COMFLOW_DIR/python. The actual plugins are provided
by the Python module comflow.paraview.plugins for which the Python file CMFPlugins.py
provides an entry point.
Two steps are required for installing the ComFLOW Paraview plugins:
Add the subdirectory
$COMFLOW_DIR/pythonto the Python search pathPYTHONPATH. This step may be skipped if the ComFLOW environment module or bash setup script is used.Configure the plugins:
Generate a Paraview plugin configuration file (XML) by running the provided Python script, as follows:
python $COMFLOW_DIR/python/generate_plugin_config_file.pyAdd the location of the plugin configuration file (
$COMFLOW_DIR/python/paraview_plugins.xml) to the Paraview environment variablePV_PLUGIN_CONFIG_FILE. This step may be skipped if the ComFLOW environment module or bash setup script is used.
Alternatively, the plugins may be configured manually by using the menu “Tools/Manage plugins” in the Paraview GUI. Here, add the Python file
$COMFLOW_DIR/python/CMFPlugins.pyand optionally select the auto-load option.
3.5. Installing the MATLAB pre- & post-processor¶
After having unpacked the ComFLOW deliverables the MATLAB pre- & post-processor is located in the subdirectory matlab.
In order to install the ComFLOW-MATLAB application perform the following steps:
Start matlab.
Open (or create) the MATLAB user start-up script by typing
edit startup.m. This file should be placed on the user path (typeuserpathin the command window to see where).Copy and paste (add) the contents of the file
cmf_startup_template.mto the startup script opened in step 2a.To set (or change) the version, run the MATLAB script
cmf_select_this_version.m. This file is located in the directorymatlab/postpr.NB: Do not move this script to any other location because this may undo the installation.
Restart MATLAB.
The ComFLOW pre- & post-processor can now be opened by typing comflow in the MATLAB command window.
A separate manual is provided for the use of this program.
3.6. Performing a test run¶
In the subdirectory examples a set of small-sized simulations is included for testing and illustration purposes.
To see if the ComFLOW package is installed correctly, try to run one of the example simulations:
- open a console (Linux) or the ComFLOW command prompt (Windows)
- change to the sub-directory
examples - then change directory to the example of choice
- most of the examples can be run by subsequently typing
geodef,comflow(several examples require additional steps which are explained in the relevant sections of the manual) or by using theruncomflowPython script.
To see if the Paraview plugins and/or the MATLAB pre- & post-processor are installed correctly, after having run a simulation try to display a snapshot or monitor file.
3.7. The different parts of ComFLOW¶
3.7.1. The pre-processor GEODEF¶
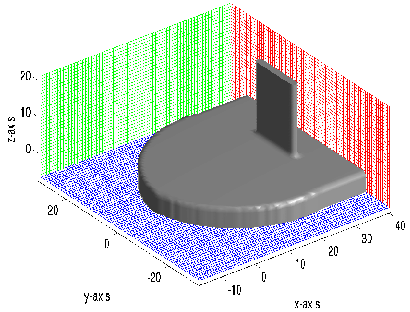
The pre-processor GEODEF should be run first. After running GEODEF (which should take no more than a minute), the resulting geometry and the grid can be plotted using the ComFLOW pre-processor in MATLAB. The result of the example case is shown in Fig. 3.1.
3.7.2. The pre-processor WAVE51¶
Note
The WAVE51 functionality has been replaced by a new shared-library/DLL-based approach that does no longer require pre-processing. More details can be found in Section 26.2.1.
3.7.3. The flow solver ComFLOW¶
Now everything is prepared for the first run of the flow solver
ComFLOW.
The input files needed by ComFLOW are apertures.in (which is produced by GEODEF) and comflow.in. The first results can
already be visualized during the simulation, see the next section.